Infrared laser material
Infrared thermal imaging technology has gradually developed from the initial military "night vision" application to various fields such as medical treatment, industry, homeland security, public security, fire protection, electric power, automobile application, etc. With the maturity of infrared thermal imaging technology and the reduction of manufacturing cost, the application field of infrared thermal imager in the civil market is constantly expanding, and it is expected that the growth space of civil infrared thermal imager will be huge in the future.Infrared thermal imaging technology uses infrared detector and optical imaging objective to receive the infrared radiation energy distribution of the target to be measured, and reflect it to the photosensitive element of the infrared detector.
With the maturity of infrared thermal imaging technology and the reduction of manufacturing cost, infrared thermal imager is expanding in the civil market, and the development potential of civil infrared thermal imaging is huge in the future.
Main item:
germanium, Zinc selenide
silicon, Gallium arsenide
Germanium, Zinc selenide
Zinc sulfide
silicon
Chalcogenide glasses
Crystal
Distribution of Crystal is very wide, the vast majority of natural solid matter is crystal. Gases, liquids and amorphous materials can also be transformed into crystals under certain suitable conditions. Products are widely used in laser medical beauty, laser industrial processing, LED, RFIC, wearable device, smartphone.Feature:
1. Long range order: the regular arrangement of atoms in the crystal within the range of at least micrometers.
2. Uniformity: the macroscopic properties of each part in the crystal are the same.
3. Anisotropy: the crystal has different physical properties in different directions.
4. Symmetry: the ideal shape and internal structure of the crystal have specific symmetry.
5. Self limitation: the crystal has the property of spontaneously forming a closed geometric polyhedron.
6. Cleavage: the crystal has the property of cleavage along certain orientation.
7. Minimum internal energy: the minimum internal energy of molding crystal.
8. Conservation of crystal face angle: the angle between two corresponding crystal faces belonging to the same crystal is constant.
Maim item:
Nonlinear KTP crystal, Potassium Niobate Crystal, Electro Optical RTP Crystals
Cesium Lithium Borate Crystal (CLBO ), NaI(Tl) Crystal, Calcium Fluoride Crystal
Magnesium Fluoride Crystal, KTA crystal, LBO crystal, BBO crystal
DKDP / KDP crystal, Nd:YAG crystal, Bonds and crystals
Substrates
Used for production of various film materialsMain item:
Strontium titanate (SrTiO3)
Barium titanate (BaTiO3)
Lanthanum aluminate (LaAlO3)
Aluminic acid lithium/ gallium acid lithium (LiGaO2/ LiAlO2)
Gadolinium gallium garnet (GGG)
Lanthanum aluminate .Strontium aluminium tantalate (LSAT)
Magnesium oxide (MaO)
Zirconia (ZrO2)
Sapphire (AlO3)
Ceramic (alumina, aluminum nItride, zirconia, Silicon nitride)
Semiconductor
Magnetic and ferroelectricity
High temperature superconducting
Sputtering Target
The target material of coating is the sputtering source which forms various functional films on the substrate by magnetron sputtering, multi arc ion plating or other types of coating system under appropriate technological conditions. In short, the target material is the target material bombarded by high-speed charged particles. When used in high-energy laser weapons, different power density, different output waveforms, different wavelengths of laser interact with different target materials, it will produce different damage effects. For example: evaporation magnetron sputtering coating is heating evaporation coating, aluminum film, etc. By replacing different target materials (such as aluminum, copper, stainless steel, titanium, nickel targets, etc.), different film systems such as super hard, wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant alloy films can be obtained.Main item:
Monocrystalline target
Metal target
Alloy target
Ceramic target
Heat sink materials
Used for heat dissipation in electronic packaging industry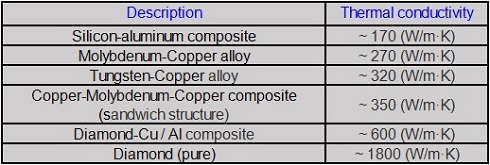
Special Glass
Main item:ITO, AZO, FTO . One way perspective glass
high pressure resistant glass, high temperature resistant glass
high temperature resistant glass, fireplace glass
wave soldering glass, oven glass, high temperature and high pressure resistant glass UV transparent glass
optical glass, blue cobalt glass, laser protective glass
welding protective glass, glass tube, high aluminum glass
aluminum silicate glass, ceramic glass
Metals And Alloys
Iron, chromium, manganese, aluminum, magnesium, potassium, sodium, calcium, strontium, barium, copper, lead, zinc, tin, cobalt, nickel, antimony, mercury, cadmium, bismuth, gold, silver, platinum, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium, beryllium, lithium, rubidium, cesium, titanium, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, niobium, tantalum, tungsten, molybdenum, gallium, indium, thallium, germanium, rhenium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium scandium, yttrium, silicon, boron, selenium, tellurium, arsenic, thorium.Aluminum alloy, copper alloy, zinc alloy, magnesium alloy, lead-tin alloy
titanium alloy, ferroalloys, potassium sodium alloy, ferrosilicon, ductile iron
steel, stainless steel, ferromanganese
brass, bronze, white copper, soldering tin, duralumin
Magnetic material
Materials that can react to magnetic fields in some way are called magnetic materials. According to the magnetic strength of substances in the external magnetic field, they can be divided into diamagnetic substances, paramagnetic substances, ferromagnetic substances and antiferromagnetic substances. Most materials are diamagnetic or paramagnetic, and their response to external magnetic field is weak. For magnetic materials, magnetization curve and hysteresis loop are characteristic curves reflecting their basic magnetic properties. Ferromagnetic materials are generally Fe, Co, Ni elements and their alloys, rare earth elements and their alloys, and some Mn compounds. According to the difficulty of magnetization, magnetic materials are generally divided into soft magnetic materials and hard magnetic materials.Main item: sintered / bonded permanent ferrite powder, bonded samarium cobalt magnetic powder, bonded NdFeB magnetic powder, NdFeB magnetic stripe.
CVD tubular furnace for graphene grown on metal foil substrate
application: used to prepare graphene and various two-dimensional materialsquartz tube diameter: Φ50mm / Φ60mm / Φ80mm / Φ100mm
working temperature: 1150 ℃
single-phase alternative current: 220V, 50Hz
maximum heating and cooling rate: 20 ℃/min
pressure: 10-2Pa
heating zone: 400mm
constant temperature zone: 200mm
temperature control accuracy: ± 1 ℃
applicable carbon source: various dry and wet carbon sources


CVD equipment for mass production of graphene
application: mass production of graphenequartz tube diameter: Φ250-550mm
working temperature: 1150 ℃
single-phase alternative current: 220V, 50Hz
maximum heating and cooling rate: 20 ℃/min
pressure: 10-2Pa
heating zone: 400mm
bconstant temperature zone: 1000mm
copper foil running speed: 100-400mm/min, adjustable
temperature control accuracy: ± 1 ℃
applicable carbon source: methane


Copyright © 2012 Beijing Zhong Tuo Material Technology Co., Ltd. All rights reserved